Campo de arroz
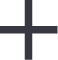
operação de mecanização de todo o processo
Produtos recomendados

Trator de rodas RX804

1GQN-250
Cultivador rotativo

RS130-160HP
Trator de rodas

1GQN-250
Cultivador rotativo

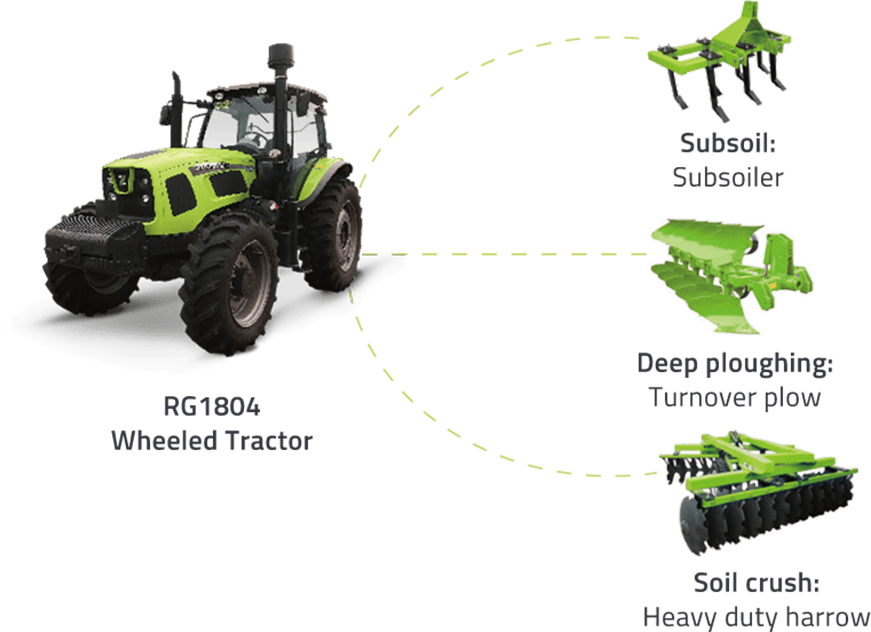
Agrotechnical requirements:
The general plowing depth is 22-25 cm; the field should be fine and flat after the operation, so as to facilitate shallow irrigation, and the field should be leveled again after irrigation and beating.
Mechanized tillage and soil preparation technology:
Combining the local agronomic requirements with the soil condition of this farm, it is recommended to adopt shallow plowing by rotary tiller. This aims to return the crop straw to the field while ensuring that the soil layer is not damaged.
Produtos recomendados

RC90-110HP
Wheeled Tractor

1205
5 rows of sowing

RS130-160HP
Wheeled Tractor

1405
8 rows of sowing

Requisitos agronômicos para a semeadura:
Semeadura no momento certo: o solo ou canteiro deve estar liso e macio, com umidade adequada.
Taxa de semeadura: a taxa de semeadura por mu é geralmente de 3 a 5 kg, ou seja, 3.000 a 5.500 mudas básicas por mu. A quantidade real de mudas é determinada pelas características das variedades locais.
Espaçamento entre linhas de semeadura: a distância entre linhas equidistantes geralmente é de 50 a 70 cm.
Espaçamento de plantio: 60 a 70 cm.
Profundidade de semeadura: 5 a 6 cm, sendo a profundidade máxima inferior a 10 cm.
Requisitos agronômicos para fertilização:
Fertilização regular: A aplicação profunda da fertilização da semente é de 5 a 8 cm abaixo da semente e cerca de 5 cm ao lado da semente.
Técnicas de semeadura e fertilização:
A tecnologia mecanizada de semeadura de milho é adotada para concluir as operações de fertilização profunda, semeadura, cobertura do solo, sulcamento e prensagem ao mesmo tempo.
Recommended products
-

Aspersor de bico único tipo carretel máquina de irrigação
-

Aspersor de bico único tipo carretel máquina de irrigação
-

Aspersor de bico único tipo carretel máquina de irrigação
O negócio de gerenciamento de campo inclui principalmente pulverização e irrigação,
e as principais máquinas e ferramentas são máquinas de pulverização e equipamentos de irrigação.
|
Management stage |
Purpose |
Time |
Actions |
Required machines |
|
Pre-seedling |
Ensure the |
From seedling |
>Using herbicide |
Spraying machines |
|
Seedling |
Ensure the |
From seedling |
>Preventing diseases, insect pests |
Spraying machine and irrigation |
|
After-seedling management |
Promote the stem and seedling |
From jointing to harvest-before |
>Use ear-fertilizer |
Spraying machine and irrigation |
Recommended products

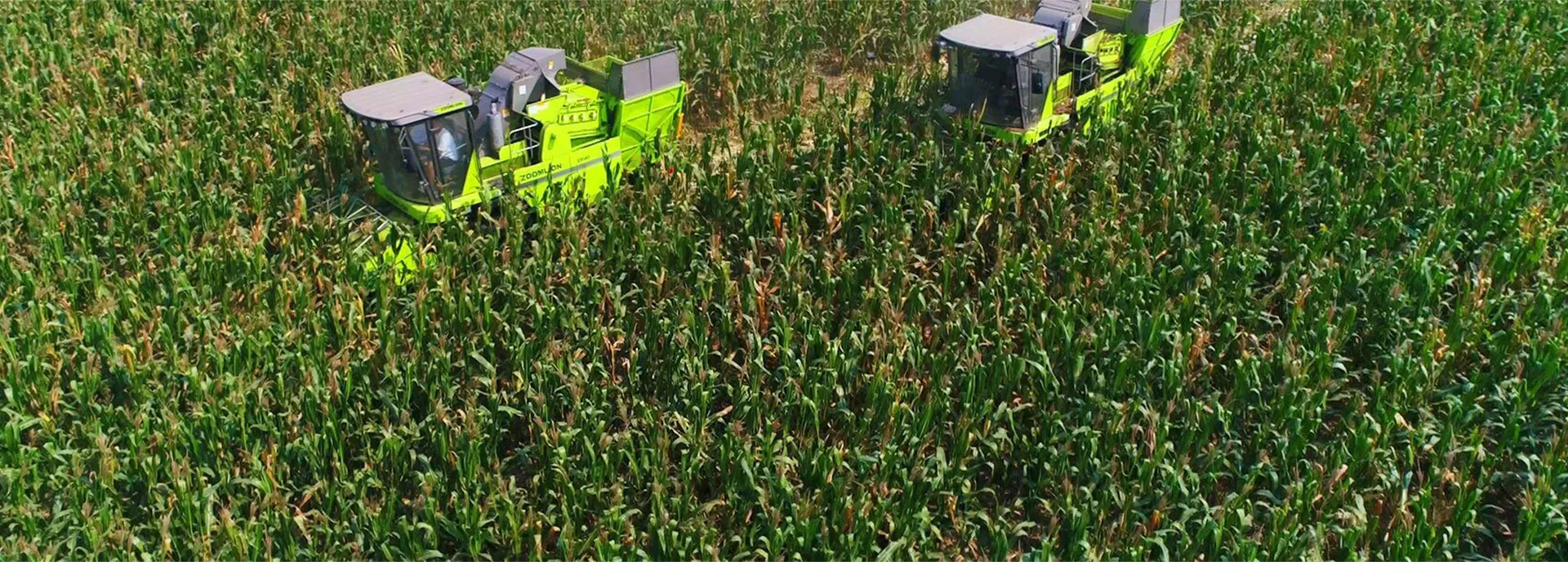
TE100 Wheeled Combine Harvester
Modo de transporte:
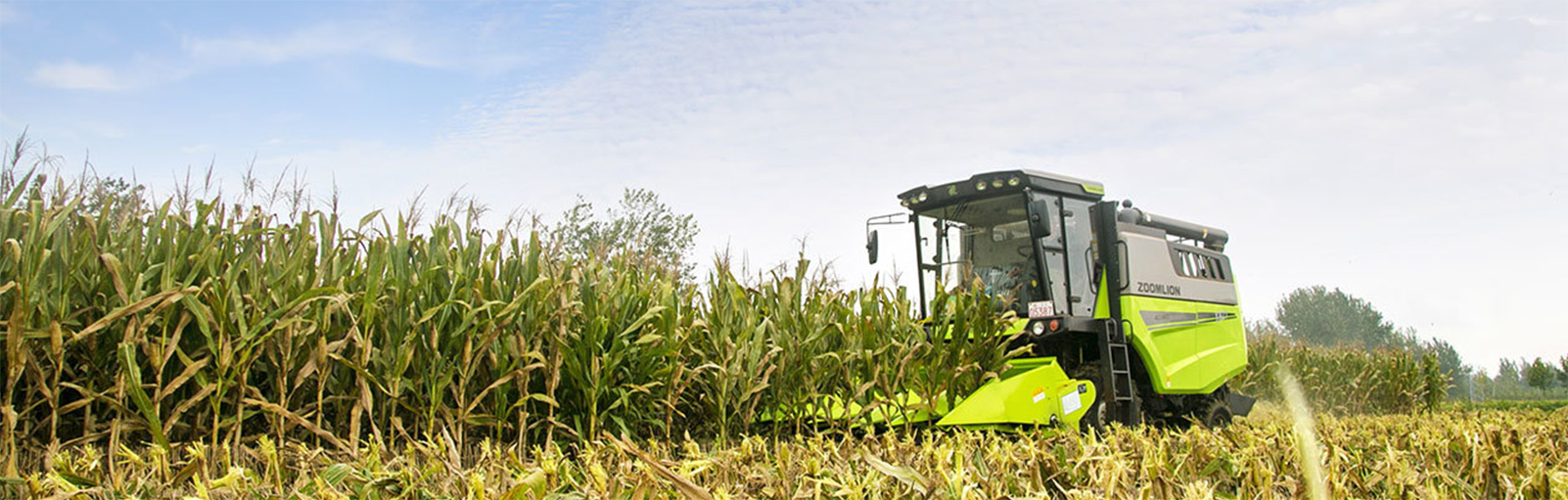
A colheitadeira mecânica de milho é uma combinação da tecnologia de mecanização do milho, podendo ser utilizada para colheita, transporte, empilhamento, tratamento de palha e outras operações.
A colheitadeira de milho autopropelida possui as vantagens de estrutura compacta, desempenho impecável, alta eficiência operacional e boa qualidade de operação, o que representa uma tendência de desenvolvimento. Atualmente, a tecnologia deste tipo de produto está gradualmente desenvolvida e madura, com ampla gama de promoção e aplicação.
Requisitos agronômicos:
Taxa de perda de grãos ≤ 2%, taxa de perda de grãos ≤ 3%, taxa de quebra de grãos ≤ 1%, altura do restolho ≤ 8 cm,
teor de umidade abaixo de 20% na debulha do milho, comprimento do corte da palha ≤ 5 cm,
taxa irregular de lançamento da palha ≤ 20%.
Recommended products

Trator de rodas RX804

Rotary tiller

Beating-leveler
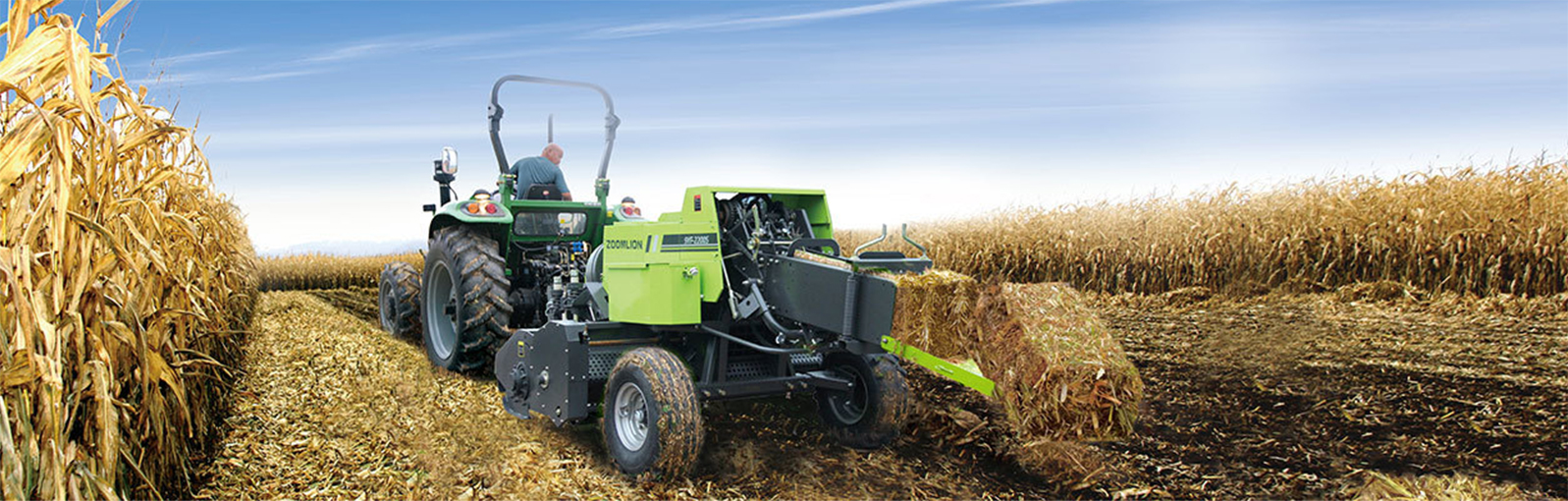
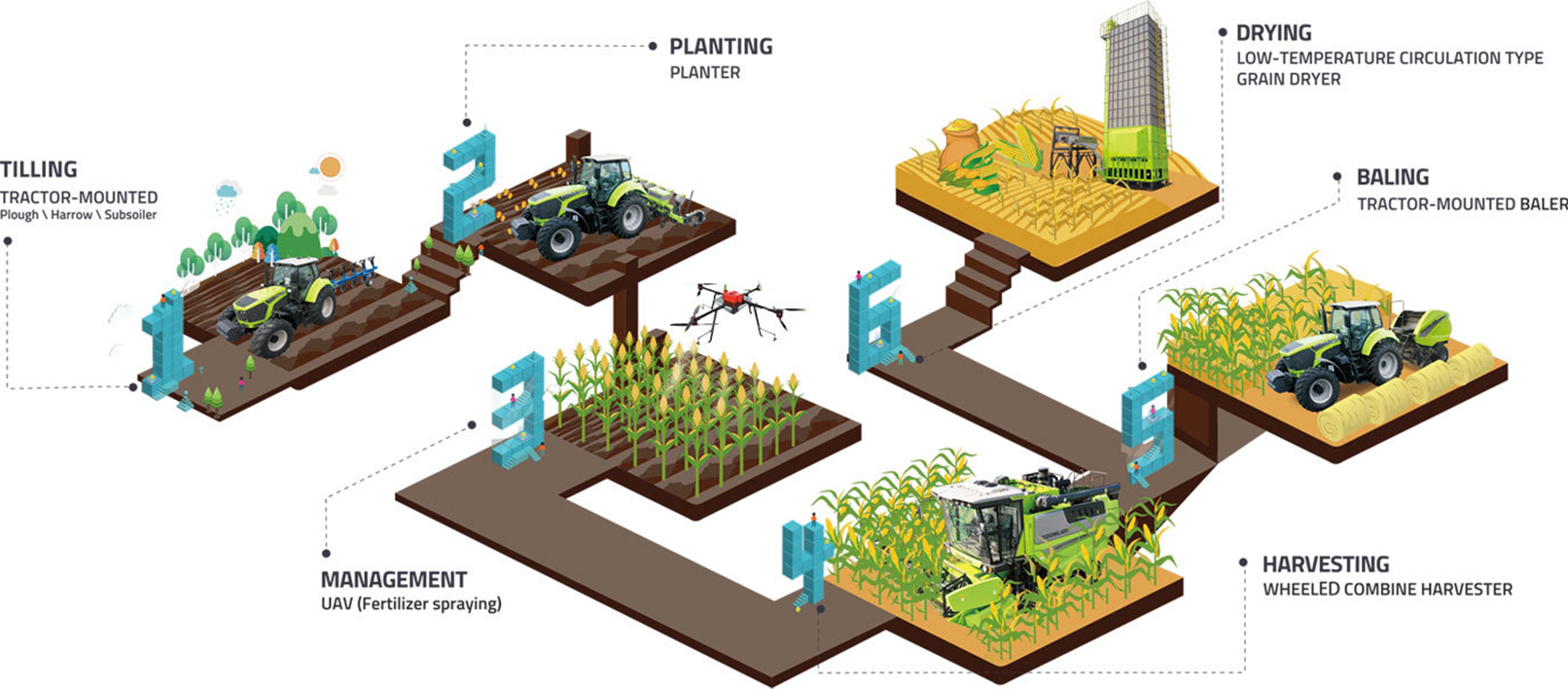
The straw post-processing refers to the use of machinery to crush, bury, or bale the harvested rice straw for recycling, which is conducive to reducing environmental pollution, enhancing soil fertility, and increasing grain output.
Technical route of rice straw post-processing:
After the rice is harvested, the straw is baled and recycled for use as feed or biomass.
Recommended products
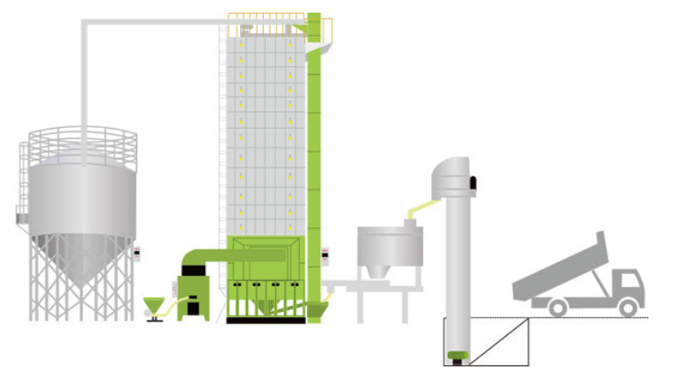
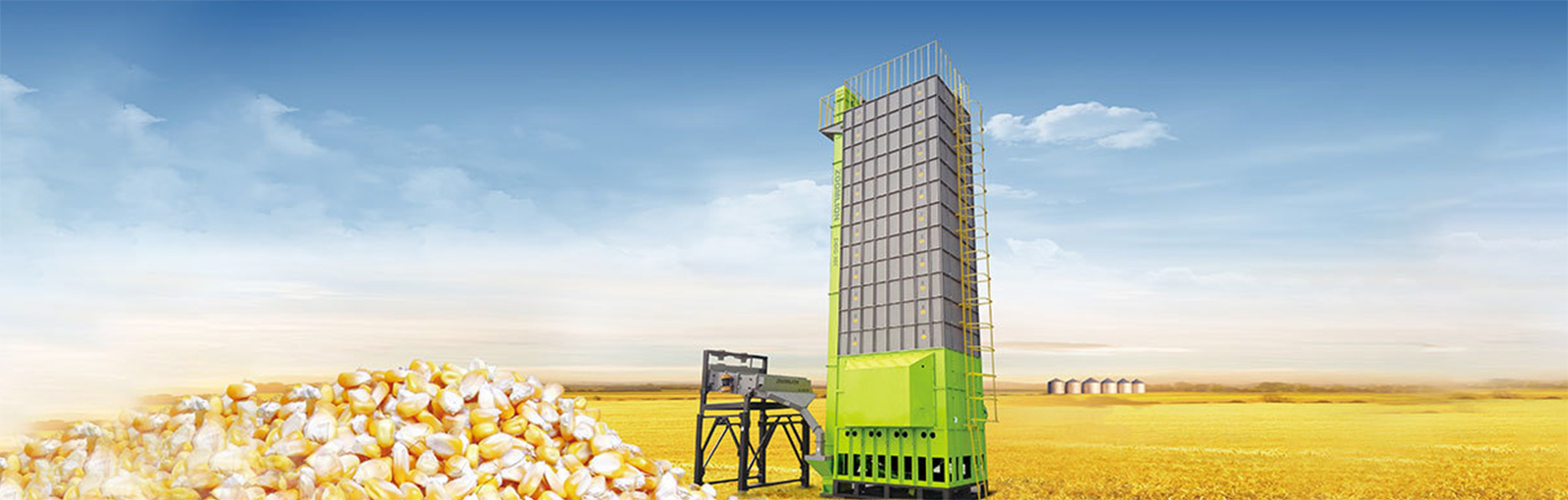
Grain drying center
Harvesting post-treatment mainly refers to the drying and the other operations on the harvested corn to facilitate storage and processing.
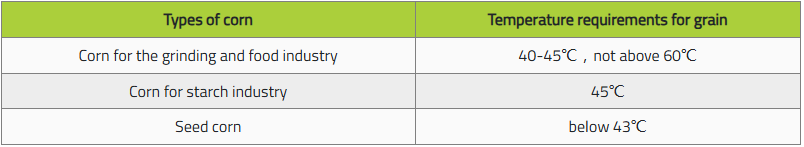
Requirements of the corn dryer
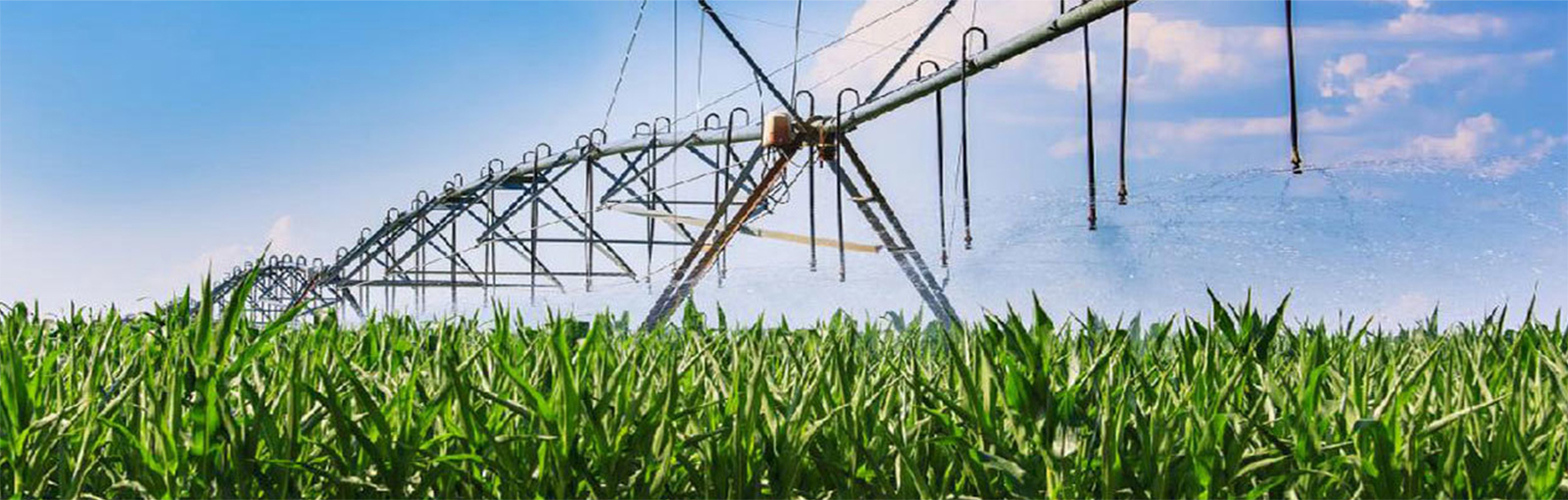
Irrigation:
Sugarcane is one of the most water-demanding crops and water availability is the single largest factors affecting its yield. As water is the basis of physiological activities, the normal and vigorous physiological and biochemical processes, the fast growth and the high yield of the sugarcane are all dependent upon an appropriate water availability.
As a low water availability in the sugarcane field will restrict the growth and yield of sugarcane, irrigation is very important for a higher yield. According to experiments and production experience, a reasonable irrigation has a significant effect on yield increase, which becomes more obvious in drought years.
Sugarcane has essentially four-growth phases: germination phase, tillering (formative) phase, grand growth phase and maturity & ripening phase, and the water demand of each phase is the basis to determine the irrigation time and irrigation volume.
-

Sprinkler irrigation system
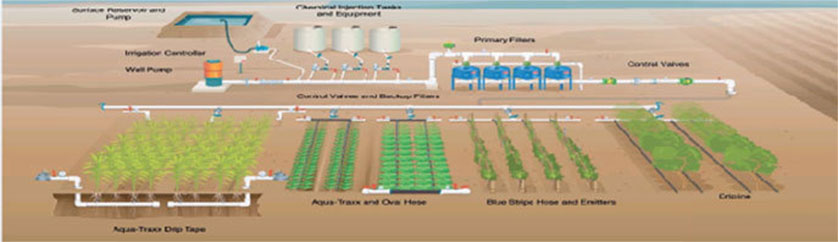
Sprinkler irrigation system
-

Drip irrigation system
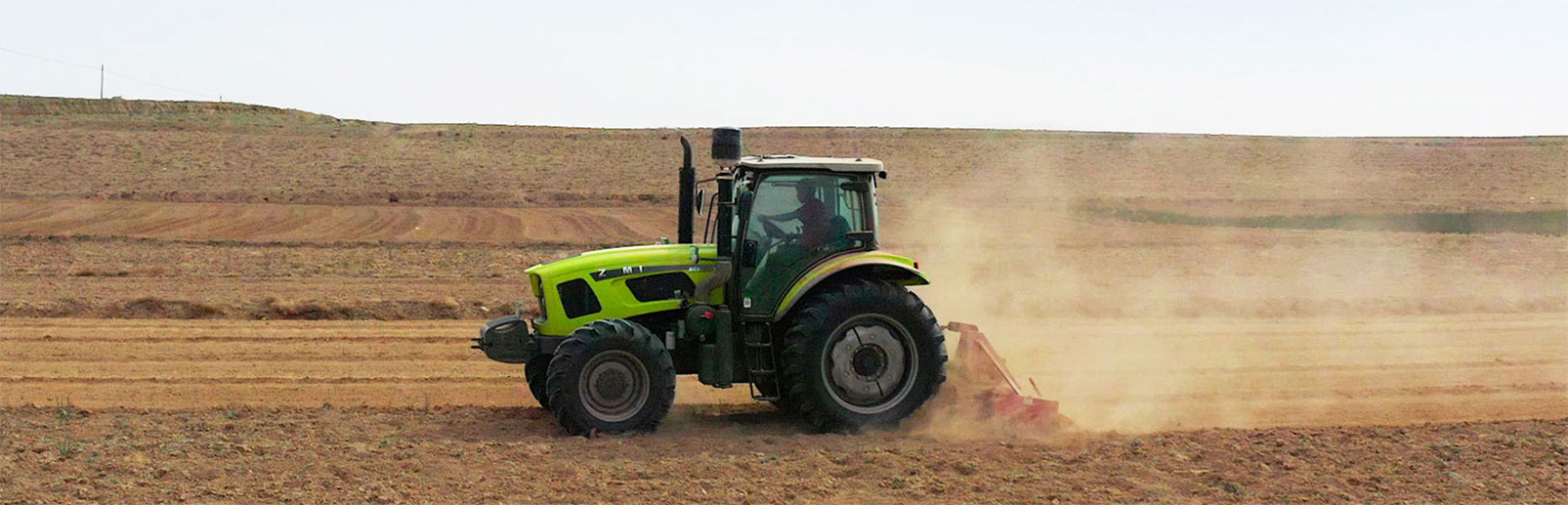
Tilling
Tractor-driven
plough\harrow\furrower
Recommended products